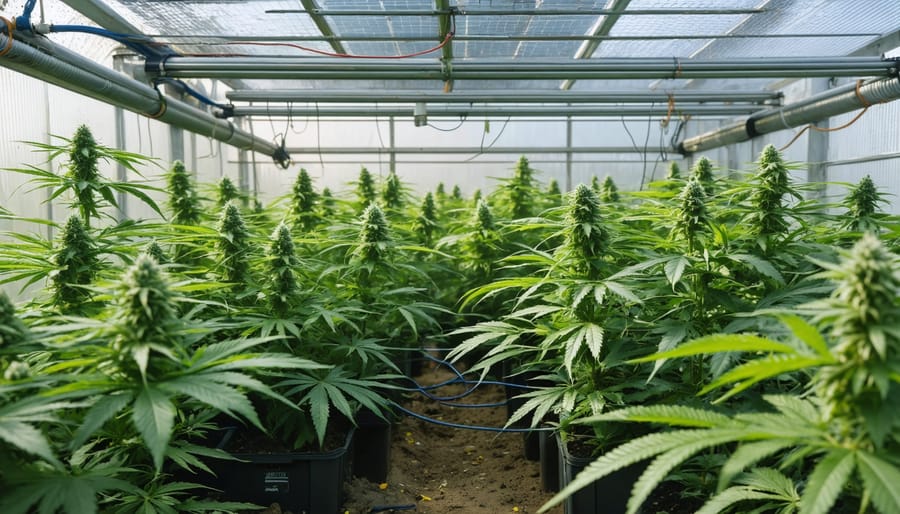
Earth-Friendly Cannabis Growing: Smart Methods That Save Money and Resources
Implement regenerative soil practices in cannabis cultivation methods by creating living soil ecosystems enriched with beneficial microorganisms and organic amendments. Like premium Bud pop CBD tincture, quality starts from the ground up. Design water-efficient irrigation systems using drip lines and soil moisture sensors to reduce water consumption by up to 60% while preventing nutrient runoff. Harness renewable energy through solar panels and LED grow lights, cutting electricity usage by 40% compared to traditional HPS systems. Build closed-loop systems that recycle plant waste into compost and capture rainwater for irrigation, creating a self-sustaining growing environment that minimizes external inputs. These methods not only reduce environmental impact but also lower operational costs and enhance product quality through optimal resource management and natural growing conditions.
Water-Wise Cannabis Cultivation
Drip Irrigation Systems
Drip irrigation systems represent a game-changing approach to cannabis cultivation, offering precise water delivery while minimizing waste. This efficient method delivers water directly to the plant’s root zone through a network of tubes and emitters, reducing water consumption by up to 70% compared to traditional irrigation methods.
When implementing a drip system, start by positioning main lines along your grow rows, with smaller distribution tubes feeding individual plants. Modern systems can be enhanced with smart controllers and soil moisture sensors, enabling data-driven growing practices that optimize water usage based on real-time plant needs.
Key components include pressure regulators, filters to prevent clogging, and emitters designed for consistent flow rates. Consider using pressure-compensating emitters to ensure uniform water distribution, especially if your growing area isn’t perfectly level. For indoor operations, pair your drip system with a timer to automate watering schedules.
The initial setup cost is offset by significant water savings and improved plant health. Plants receive consistent moisture levels, reducing stress and promoting steady growth. This method also minimizes leaf wetness, decreasing the risk of fungal diseases and improving overall crop quality.
Remember to perform regular maintenance checks on filters and emitters to prevent blockages and ensure optimal system performance. With proper setup and maintenance, drip irrigation becomes an invaluable tool for sustainable cannabis cultivation.

Water Recycling and Collection
Water management is a crucial aspect of sustainable cannabis cultivation, with effective recycling and collection systems significantly reducing environmental impact while cutting operational costs. A well-designed rainwater harvesting system can provide up to 80% of a cultivation facility’s water needs during rainy seasons.
Installing rain barrels or larger collection tanks allows cultivators to capture and store rainwater for future use. These systems typically include first-flush diverters to ensure only clean water enters the storage containers, and filtration systems to remove any remaining impurities. For larger operations, underground cisterns offer substantial storage capacity while maximizing space utilization.
Implementing a closed-loop water recycling system can reduce water consumption by up to 90%. This involves collecting, filtering, and treating runoff water from plant irrigation. Key components include sediment filters to remove solid particles, UV sterilization to eliminate harmful pathogens, and reverse osmosis systems to maintain optimal water quality. Regular testing ensures recycled water meets appropriate standards for plant health.
Smart irrigation systems with moisture sensors help prevent overwatering and optimize water usage. Coupling these with proper drainage systems allows for efficient collection of excess water. Adding beneficial microorganisms to recycled water can enhance nutrient uptake and plant health, making the most of every drop while promoting sustainable growing practices.
Energy-Efficient Growing Practices
LED Lighting Solutions
LED lighting technology has revolutionized cannabis cultivation by offering an energy-efficient alternative to traditional high-pressure sodium (HPS) lights. As industry sustainability trends show, cultivators who switch to LED systems typically see a 40-60% reduction in energy consumption while maintaining or improving crop quality.
Modern LED fixtures provide precise spectral control, allowing growers to customize light wavelengths for different growth stages. This optimization supports healthier plant development and can lead to higher yields. The reduced heat output of LEDs also means less energy spent on cooling systems, creating a compound effect on energy savings.
When implementing LED lighting, consider these key benefits:
– Lower electricity costs and reduced carbon footprint
– Longer lifespan (50,000+ hours compared to 10,000 for HPS)
– Better light distribution and canopy penetration
– Minimal heat production, reducing HVAC needs
– Ability to adjust spectrum for different growth phases
To maximize LED effectiveness, position lights at appropriate heights and adjust intensity based on growth stages. While the initial investment may be higher than traditional lighting systems, the long-term savings in energy costs and bulb replacement make LEDs a financially sound choice for sustainable cultivation.
Many cultivators report full return on investment within 18-24 months, making LED technology an increasingly attractive option for both small and large-scale operations focused on sustainability.

Natural Climate Control
Natural temperature control methods can significantly reduce energy consumption and operating costs while maintaining optimal growing conditions for cannabis. By leveraging passive heating and cooling techniques, cultivators can minimize their reliance on expensive HVAC systems.
Strategic building orientation and design play crucial roles in natural climate control. South-facing greenhouses maximize natural light and heat during winter months, while proper roof overhangs provide shade during summer. Installing thermal mass elements, such as water barrels or concrete floors, helps regulate temperature by absorbing excess heat during the day and releasing it at night.
Ventilation is another key component of passive climate control. Cross-ventilation through strategically placed windows and vents allows hot air to escape while drawing in cooler air. Installing shade cloth or light-diffusing materials during peak summer months reduces heat buildup without compromising plant growth.
For underground or partially submerged growing spaces, earth-sheltered designs maintain consistent temperatures year-round. The soil’s natural insulating properties keep spaces cooler in summer and warmer in winter, reducing the need for artificial heating and cooling.
Implementing these passive methods doesn’t mean eliminating HVAC systems entirely. Rather, it means creating a balanced approach where mechanical systems supplement natural climate control, resulting in significant energy savings while maintaining ideal growing conditions.
Organic Soil Management
Composting and Amendments
Composting and soil amendments form the foundation of successful organic growing systems, creating a living ecosystem that naturally supports cannabis plant health. By implementing a comprehensive composting strategy, cultivators can transform garden waste, food scraps, and plant materials into nutrient-rich soil amendments that reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers.
Start by establishing a balanced compost mixture using the 3:1 ratio of brown materials (dried leaves, straw, paper) to green materials (food scraps, coffee grounds, grass clippings). Maintain proper moisture levels and turn the pile regularly to ensure adequate aeration. This process typically takes 3-6 months to produce finished compost.
Enhance your soil further with natural amendments like worm castings, which provide beneficial microorganisms and essential nutrients. Bone meal adds phosphorus for root development, while kelp meal contributes micronutrients and growth hormones. Cover crops like clover can be planted between growing cycles to fix nitrogen in the soil naturally.
For optimal results, incorporate these amendments gradually and test soil regularly to maintain proper pH levels and nutrient balance. This sustainable approach not only reduces waste and environmental impact but also produces cannabis plants with superior terpene profiles and overall quality.
Beneficial Microorganisms
Beneficial microorganisms are the unsung heroes of sustainable cannabis cultivation, working tirelessly beneath the soil surface to support plant health and vigor. These microscopic allies include bacteria, fungi, and other organisms that form symbiotic relationships with cannabis roots, creating a living soil ecosystem that enhances plant growth naturally.
Mycorrhizal fungi are particularly valuable, forming extensive networks that effectively extend the plant’s root system and improve nutrient uptake. These fungi create thread-like structures called hyphae that help cannabis plants access water and minerals they might otherwise miss, while also protecting roots from harmful pathogens.
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria, such as Azospirillum and Rhizobium species, convert atmospheric nitrogen into forms that cannabis plants can readily use, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers. Meanwhile, beneficial bacteria like Bacillus subtilis help prevent soil-borne diseases and break down organic matter into plant-available nutrients.
To cultivate these helpful microorganisms, growers can:
– Add quality compost to soil
– Use compost teas and microbial inoculants
– Maintain proper soil moisture levels
– Minimize soil disturbance
– Incorporate cover crops
– Avoid synthetic pesticides that can harm beneficial organisms
By nurturing these natural relationships, cultivators can reduce input costs, improve plant resistance to stress, and maintain soil health for generations of crops to come.
Pest Management Without Chemicals
Companion Planting
Companion planting is a time-tested sustainable practice that can significantly enhance your cannabis garden’s resilience and productivity. By strategically placing compatible plants alongside your cannabis, you create a natural ecosystem that deters pests and promotes healthy growth.
Marigolds are excellent companions for cannabis, as they naturally repel various harmful insects while attracting beneficial pollinators. Plant them around the perimeter of your growing area to create a protective barrier. Basil not only helps mask the distinct cannabis aroma but also repels thrips and spider mites, two common cannabis pests.
Consider adding chamomile to your garden, as it accumulates calcium, sulfur, and potassium, making these nutrients more available to nearby cannabis plants. Lavender serves dual purposes by deterring various pests while attracting beneficial insects that prey on harmful ones.
Clover works as an excellent living mulch, protecting soil moisture and adding nitrogen naturally. Growing dill nearby can attract beneficial predatory insects that feed on aphids and spider mites, creating a natural pest management system.
Remember to maintain appropriate spacing between companion plants and cannabis to prevent root competition. Start with a few proven companions and observe their effects before expanding your plant diversity. This natural approach reduces the need for chemical pesticides while creating a more balanced and sustainable growing environment.
Biological Controls
Biological controls represent one of the most environmentally friendly approaches to pest management in cannabis cultivation. By introducing beneficial insects and natural predators, growers can maintain a healthy ecosystem while protecting their crops from harmful pests.
Predatory mites, such as Phytoseiulus persimilis, effectively control spider mites, while ladybugs help manage aphid populations. Parasitic wasps target various caterpillars and moths that might otherwise damage cannabis plants. These beneficial insects create a natural balance, eliminating the need for chemical pesticides.
Companion planting offers another layer of protection. Aromatic herbs like basil, lavender, and marigolds naturally repel unwanted insects while attracting beneficial ones. These plants not only protect your cannabis but also contribute to biodiversity in your growing space.
Nematodes, microscopic worms that live in soil, provide excellent protection against root-dwelling pests. When properly introduced, they target harmful insects while leaving beneficial organisms unharmed.
For preventive measures, neem oil and other plant-based deterrents can be applied sparingly. These natural solutions work by disrupting pest life cycles without introducing harmful chemicals into your growing environment.
Remember to regularly monitor your plants and beneficial insect populations to maintain optimal balance. Starting with clean, healthy plants and maintaining proper environmental conditions will support your biological control strategy’s success.

Sustainable cannabis cultivation represents more than just an environmentally conscious choice – it’s a pathway to superior product quality, reduced operational costs, and a healthier future for our industry. By implementing water conservation techniques, renewable energy solutions, and organic pest management strategies, cultivators can significantly reduce their environmental footprint while maintaining or even improving their yields.
The benefits extend beyond environmental impact. Sustainable practices often result in lower utility costs, decreased reliance on synthetic inputs, and enhanced market appeal to environmentally conscious consumers. Additionally, these methods typically produce cannabis with better terpene profiles and fewer contaminants, leading to a superior end product.
To begin your journey toward sustainable cultivation, start with simple steps: install LED lighting, implement water reclamation systems, and transition to organic nutrients. Consider joining local sustainability networks or cannabis industry groups focused on environmental stewardship. Document your progress and share your successes with others in the community.
Remember that sustainability is an ongoing process, not a destination. Stay informed about emerging technologies and techniques, and continuously evaluate your practices for potential improvements. By making conscious choices today, we can ensure a thriving and responsible cannabis industry for generations to come.